MACCHING CNC is a process that uses computer programming to control machine tools for precision machining. The process flow of CNC machining parts usually includes the following main steps:
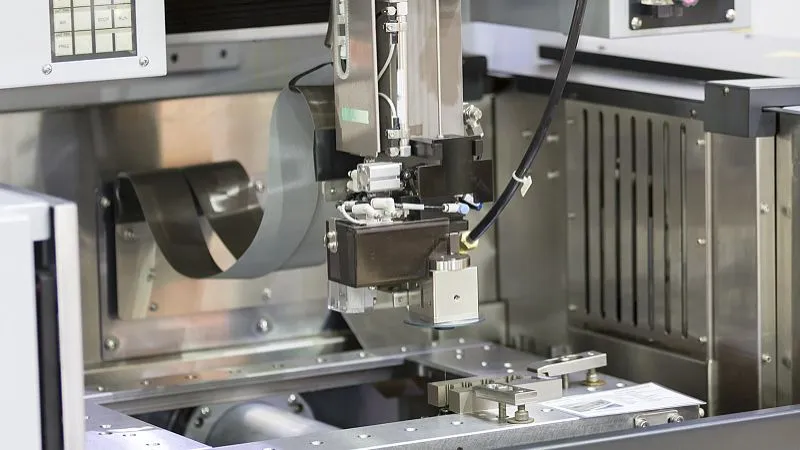

1. Design Phase
CNC machining part design: Engineers first design a 3D model of the part based on the requirements, ensuring that the design meets functional and manufacturing requirements.
Process Planning: Part process analysis is performed to determine machining methods, tool selection, and machining sequence.
2. Programming Phase
Programming: CNC machining programs are created using CAM software based on the 3D model, including tool paths, feed rates, spindle speeds, and other details.
3. Material Preparation
Material Selection: Suitable materials, such as steel, alluminio, and plastic, are selected based on the part’s functional requirements.
Material Fixturing: The material is secured to the workbench to ensure stability during machining.
4. Processing Phase
Equipment Preparation: A suitable CNC machining machine is selected and necessary equipment adjustments and preheating are performed.
Program Import: The prepared CNC machining program is imported into the machine control system.
Processing: The CNC machine is started and machining is performed according to the program. During machining, the machine’s tool moves along a predetermined path, cutting the material to form the desired part.
5. Inspection Phase
Dimensional Inspection: Dimensional inspection of completed CNC-machined parts is performed using tools such as calipers and coordinate measuring machines.
Appearance Inspection: Surface inspection of parts is performed to check for burrs, tool marks, or other defects.
6. Post-Processing Phase
Deburring: Removes burrs and sharp edges to improve the appearance and safety of parts.
Cleaning: Removes chips and coolant generated during CNC machining to maintain part cleanliness.
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment can be performed if necessary to increase part hardness or improve material properties.
7. Quality Control
Quality Inspection: Comprehensive quality inspections are conducted, including dimensional accuracy, surface roughness, and material hardness.
Performance Testing: Parts are tested for performance, such as strength and wear resistance, to ensure they meet design requirements.
8. Packaging and Shipping
Packaging: Approved parts are properly packaged to protect them from damage during transportation.
Shipping: Packaged parts are delivered to customers or sent to the next production stage.
CNC machining is a highly automated precision machining method. Its process covers the entire process from design, programming, material preparation, processing, inspection, post-processing, quality control, and finally packaging and shipping. Each step has a significant impact on the final quality and performance of the part. Perciò, strict process management and quality control are the key to the success of CNC machining parts.