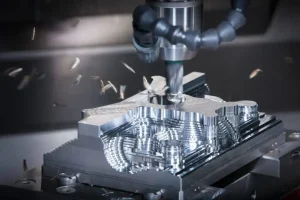
As designers draw intricate part drawings and engineers conceive groundbreaking product prototypes, a critical question arises: How can virtual designs be accurately translated into reality? At this point, CNC machining services have become a solid bridge connecting creativity and manufacturing, supporting the precision needs of modern manufacturing with their strong technical capabilities.
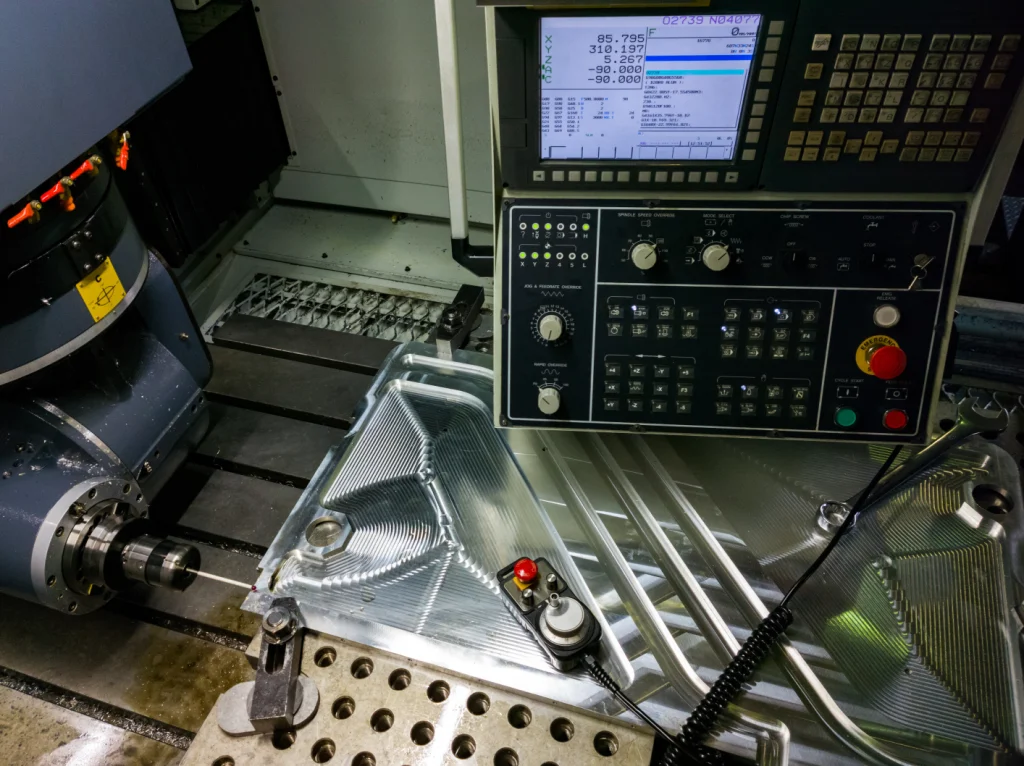

CNC: IL “Machine Conductor” of the Digital Age
The core of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lies in its digital control principle. Engineers input a 3D CAD model of the part into specialized software (CAM), which automatically generates detailed G-code instructions. These instructions are like a “musical score”, precisely controlling the tool path, feed speed, spindle speed and other parameters of the machine tool, driving the tool to accurately cut on metal, plastic, composite materials and other blanks, and finally carving out solid parts that are exactly the same as the design. This “design-driven manufacturing” model completely subverts the traditional processing method that relies on manual operation and templates.
Five Core Benefits of CNC Machining Services:
1.Precision: The Master of Micron-Level: The core competitiveness of CNC machining lies in its ultra-high precision and repeatability. Modern precision CNC machine tools can achieve positioning accuracy of ±0.005mm or even higher (much smaller than the diameter of a human hair). Whether 1 or 1000 pieces are produced, the critical dimensions of each part can be highly consistent, meeting the requirements of near-tight dimensional tolerances for aerospace precision components, medical device implants, optical instrument core lens barrels, ecc.
2.”Sculptor” of complex geometries: Five-axis linkage machining technology gives CNC unparalleled ability to process complex surfaces. The tool can move simultaneously in five degrees of freedom, easily completing complex 3D surface machining that is difficult to achieve with traditional methods, such as impellers, turbines, engine blocks, and complex mold cavities, and frees up design freedom.
3.Wide Range of Material Applications: From Aluminum to Superalloys: CNC machining services cover virtually all engineering materials that can be cut. From commonly used aluminum alloys (preferred for lightweighting), stainless steel (corrosion resistance requirements), brass/copper alloys (conductive parts), to engineering plastics (insulation, wear parts), to challenging titanium alloys (aerospace, medical implants), and superalloys (such as Inconel, for jet engines), CNC can handle it with ease.
4.Balance Efficiency and Mass Production: While small batches of single pieces are the strength of CNC (without the need for expensive tooling), CNC often outperforms traditional machining or even partial additive manufacturing in terms of efficiency for parts with complex structures or medium volumes, such as hundreds to thousands of pieces. Automated clamping, efficient tool path optimization, and multi-process integration (turning-mill combination) significantly improve efficiency.
5.Surface Finish: Più di “cutting”: Through fine cutting parameter control (e.g., speed, feed, depth of cut) and finishing strategies, CNC can directly obtain excellent surface quality (Ra value up to 0.4μm or lower), reducing subsequent polishing steps. Combined with high-speed milling (HSM), a mirror finish can be achieved on hard materials.
Core machining methods: milling, turning and compounding
CNC milling: Rotating tools cut fixed workpieces, excelling in machining planes, grooves, holes, complex contours and three-dimensional surfaces. Three-axis milling machines are the foundation, with exponential growth in four-axis (adding rotary axes) and five-axis (adding two rotating axes).
CNC turning: The workpiece rotates, fixes the tool for cutting, and is good at processing cylindrical, conical, threaded and other rotary body features. The turning center can integrate milling and drilling power heads to achieve “one-time clamping, complete turning and milling”.
Turning-milling composite machining: High-end equipment that combines turning and milling functions. The workpiece can be clamped once, and various processes such as turning, milling, drilling, tapping and even grinding can be completed. It is ideal for machining complex parts with maximum accuracy (reduced repeated clamping errors), increased efficiency, and simplified processes.
Key Considerations for Selecting Quality CNC Machining Services:
In the face of many suppliers, how to identify? The following points are crucial:
1.List of technical capabilities and equipment: Examine its core equipment (brand, model, year, precision level), whether it has the required key capabilities (such as five-axis machining, turning-milling compounding, large-scale gantry machining) and the actual measurement report of machining accuracy.
2.Material and Process Expertise: Is the supplier skilled in handling the specific materials you need? Are there any success stories on difficult-to-machine materials (titanium, superalloys) or specific processes (thin-walled machining, micromachining)?
3.Quality System Certification: Iso 9001 is the foundational threshold. For specific industries (e.g., medical ISO 13485, automotive IATF 16949, aerospace AS9100), certification is a mandatory pass.
4.Engineering Support and Communication: A good supplier should have a professional engineering team capable of conducting manufacturability analysis (DFM), optimizing designs to reduce costs, and clearly communicating technical details and potential risks.
5.Cases and Industry Experience: Examine their past projects, especially their successful experience in your or related industries, as an important basis for judging their ability to solve practical problems.
6.Transparent quotation and reliable delivery: The quotation should be clear and reasonable (based on materials, labor hours, equipment costs, management fees), clear delivery date, and have a stable and reliable delivery record.
Case Learning: CNC-Driven Innovation
A drone company: High-strength and lightweight aluminum alloy fuselage frame and precision motor base, through five-axis CNC machining to achieve complex aerodynamic shape and strict weight control, significantly improve flight performance.
A medical device company: Titanium orthopedic implants (such as intervertebral fusion devices) rely on ultra-high-precision (micron-scale) CNC machining to ensure biocompatibility and implant stability, and undergo strict aseptic cleaning treatment.
A precision instrument manufacturer: Optical platform components and complex sensor housings are CNC precision milling and turning to ensure dimensional stability and the precise fit required by the internal optical circuit/circuit.
CNC machining services have long transcended the simple “OEM” category and have become an indispensable technical partner for modern product research and development and high-end manufacturing. Understanding its core knowledge points – precision, complexity, material breadth, efficiency balance, and processing method selection – is the foundation for effectively utilizing this service, realizing design intent, and enhancing product competitiveness. In the wave of Industry 4.0 and intelligent manufacturing, CNC technology will continue to evolve, integrating automation, online inspection, and data interconnection to provide a stronger cornerstone for manufacturing innovation.