A Comprehensive Guide To Types Of Robotic Arms
RapidEfficient provides precision engineered components for the new energy industry, providing rapid prototyping and on-demand production for renewable energy and new energy applications. From new energy vehicle parts to energy storage devices, our advanced CNC machining ensures fast delivery times and top quality control to efficiently meet your unique project needs. Contact us now for an instant quote.

In This Article
Industrial Manipulators and Material Handling Solutions
The industry manipulator is a set of assisted handling equipment designed based on dynamics and ergonomics, and its operation mode is through manual button operation, by the gripping of the fixture tooling to achieve the transfer action of the object.
The general application scenarios mainly include:
- The target object is too heavy or too large to achieve manual handling
- The transfer angle and position of the target object are difficult to achieve manually
- The target object is easy to cause high loss through manual transfer
- The target object is easy to cause large manpower loss
Based on the above situation, we introduced the robot as an auxiliary handling tool to solve the problem perfectly. In this process, irregular objects, heavy objects, and special objects have achieved efficient transfer, saving and protecting manpower loss, and it’s been more and more widely used in the industrial production process.
Learn about the different types of manipulators
Programmable manipulators, often referred to as robotic arms, are advanced mechanical systems designed with joints and axes that enable both rotational and linear motion. Their core function is to control the end effector, the component that directly interacts with the environment to perform tasks such as lifting, positioning, or assembling.
These versatile manipulators have revolutionized safety and efficiency across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, logistics, construction, healthcare, and maritime operations. By automating complex or repetitive tasks, they reduce human effort and enhance precision in demanding environments.
This guide explores various types of manipulators, delving into their unique features, applications, and benefits. While some overlap exists in their use cases, each manipulator type offers distinct advantages tailored to specific industrial needs, making them essential tools for boosting productivity and maintaining safe, streamlined workflows.
Hard arm power manipulator
It is extensively employed in industrial environments for tasks demanding substantial force and precision.
Constructed for resilience, rigid arm manipulators consist of a solid, robust arm anchored to a stationary or movable foundation. They generally feature one to three axes of movement, making them suitable for applications such as heavy-duty material transport, assembly, forging, and handling hazardous substances in sectors like production, construction, and logistics.
Rigid arm fixed

Mounted on a stationary base, ideal for tasks requiring a stable, immovable platform, such as assembly lines or fixed-position material handling.
Rigid arm mobile
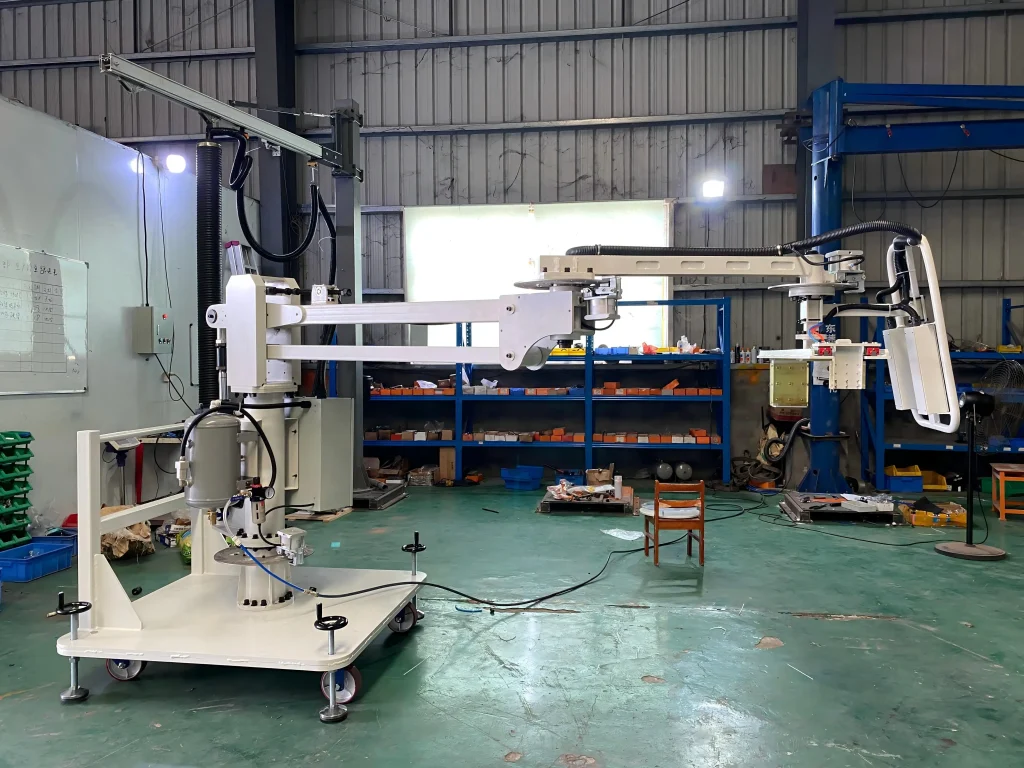

Attached to a movable base, allowing flexibility to relocate the manipulator within a workspace, suitable for dynamic environments like logistics or construction sites.
Rigid arm suspension
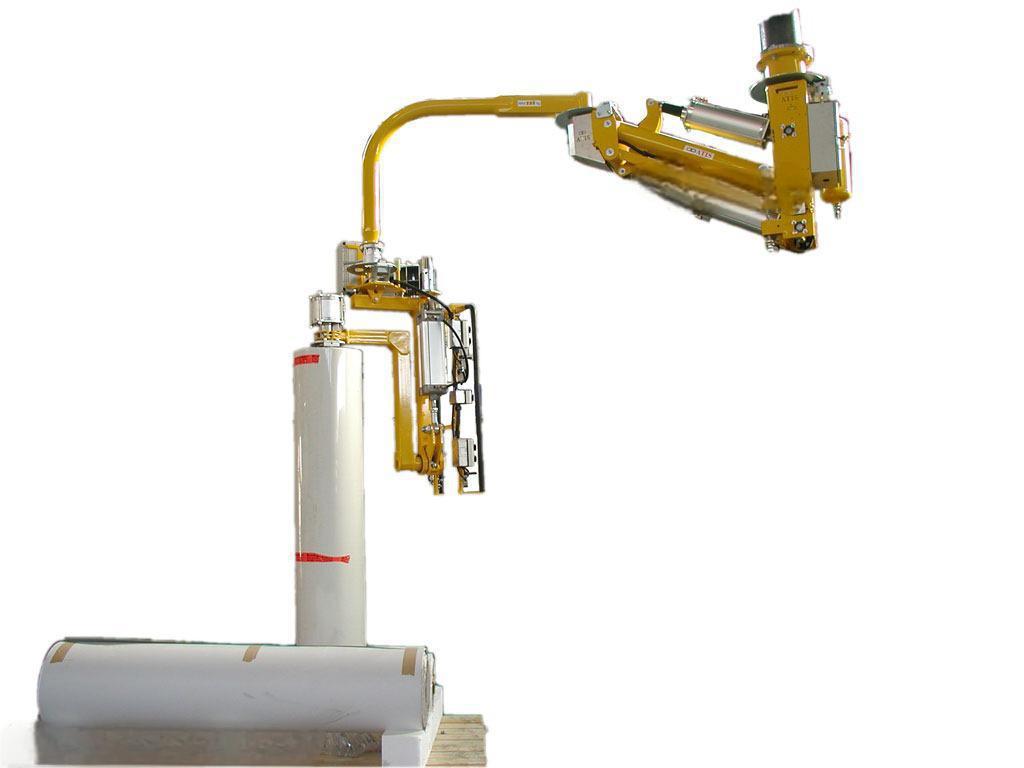

Suspended from an overhead structure, providing versatility in confined spaces or for tasks requiring elevated positioning, such as overhead material handling or forging operations.
Soft rope assist mechanical equipment
Also known as cable-driven systems or rope-based mechanisms, soft rope powered mechanical equipment operates using flexible ropes to control movement across multiple directions, resembling a dynamic coordinate system. These systems enable smooth motion along various axes, making them perfect for tasks requiring adaptability within a defined area. They are valued for their versatility, precision, lightweight design, and ability to cover large workspaces, making them ideal for applications like lifting, towing, or securing loads in construction, rescue, and maritime operations.
Horizontal cylinder type - double joints

Utilizes a horizontal cylinder mechanism with dual joints for enhanced flexibility, ideal for precise load positioning in construction or material handling tasks.
Electric intelligent balance crane - double joints
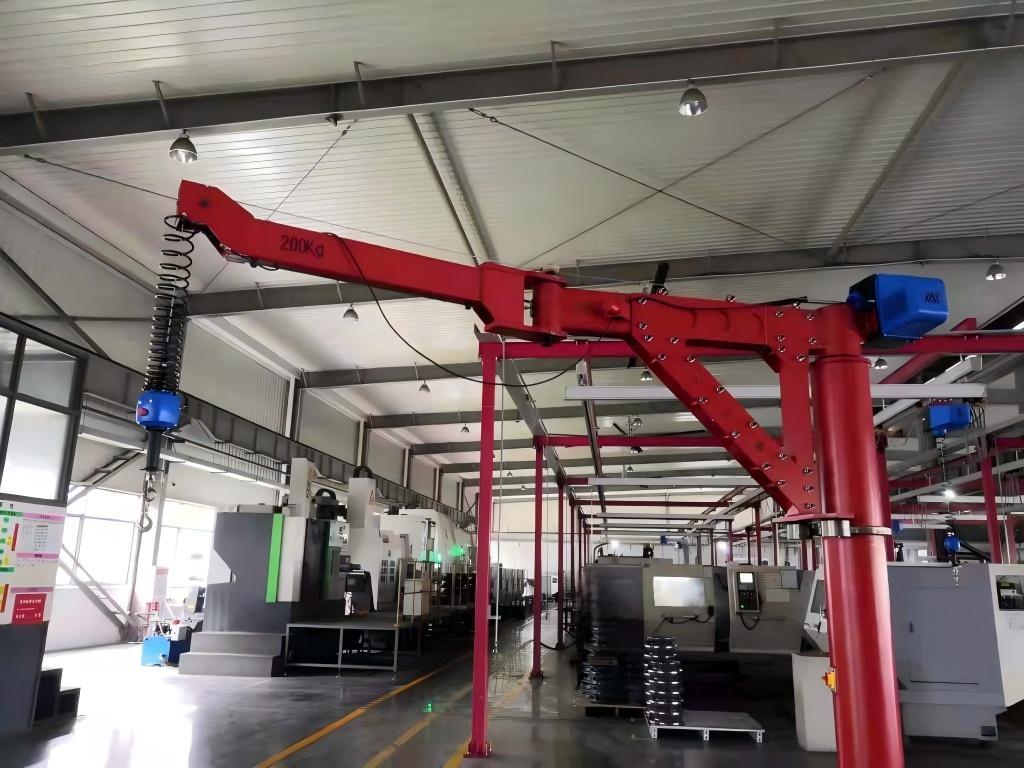

Features an electrically powered crane with intelligent balance control and dual joints, perfect for automated lifting and precise load management in industrial environments.
Pneumatic balance crane - double joints
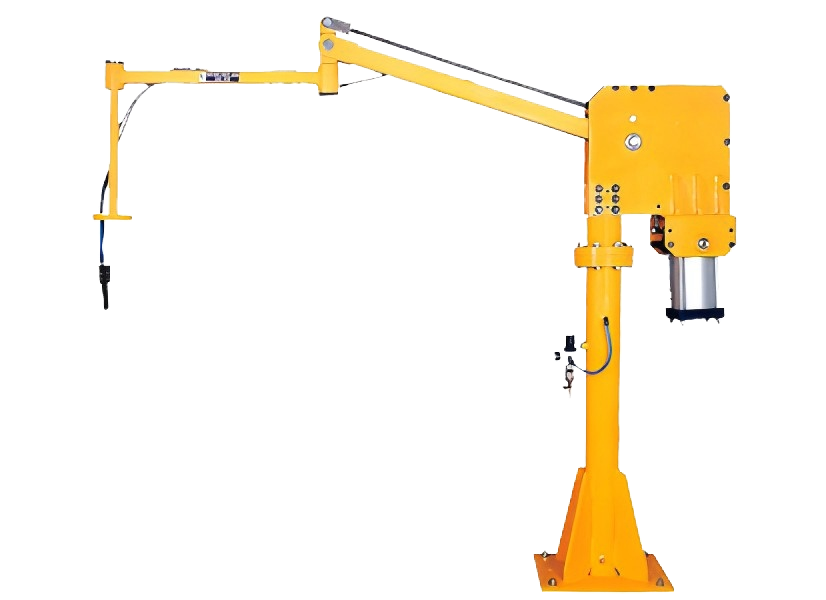
Employs pneumatic power with dual joints for smooth, controlled movements, suitable for lifting and maneuvering loads in settings like maritime or rescue operations.
Single joint-powered manipulator
Also known as single-axis manipulators or pivot arm systems, single joint-powered manipulators operate using one rotational joint to control movement, resembling a focused pivot system. These devices enable precise motion along a single axis, making them perfect for tasks requiring simplicity within a specific range. They are valued for their efficiency, precision, compact design, and ability to handle targeted tasks, making them ideal for applications like lifting, positioning, or transferring materials in manufacturing, assembly, and warehousing.
Ordinary hoist type - single joint
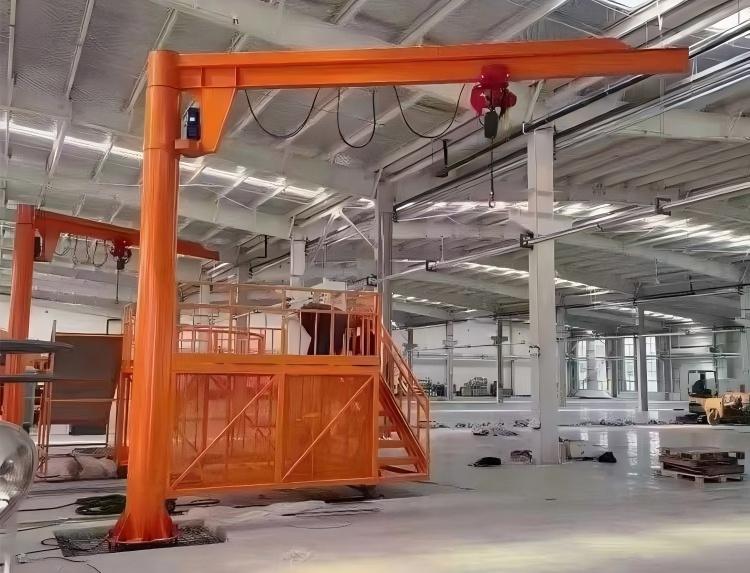

A basic hoist system with a single joint, ideal for simple lifting tasks in fixed positions, such as in small-scale manufacturing or assembly lines.
Intelligent balance crane - single joint
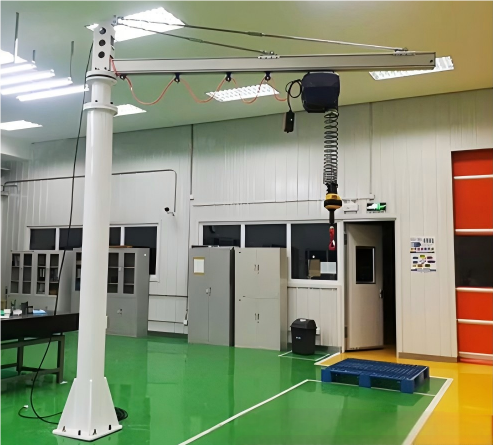

An electrically powered crane with intelligent balance control and a single joint, perfect for precise, automated lifting in industrial settings.
Pneumatic hoist balance crane - single joint
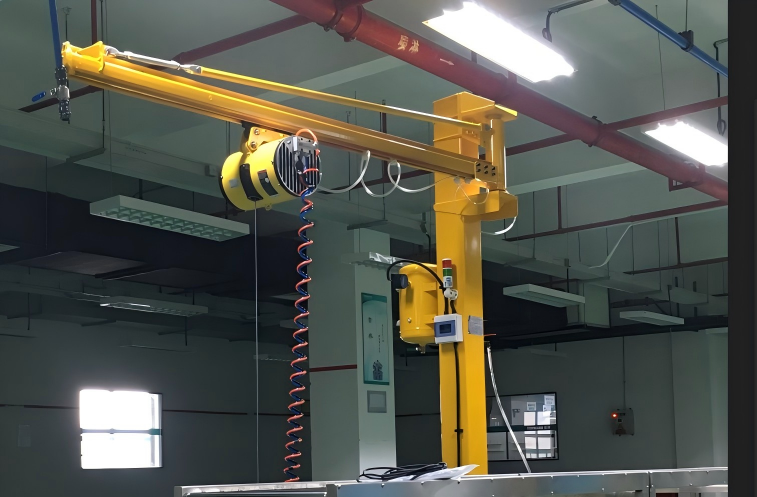

Utilizes pneumatic power with a single joint for smooth, controlled lifting, suitable for handling materials in environments like warehousing or maintenance operations.
Vacuum lifting machine
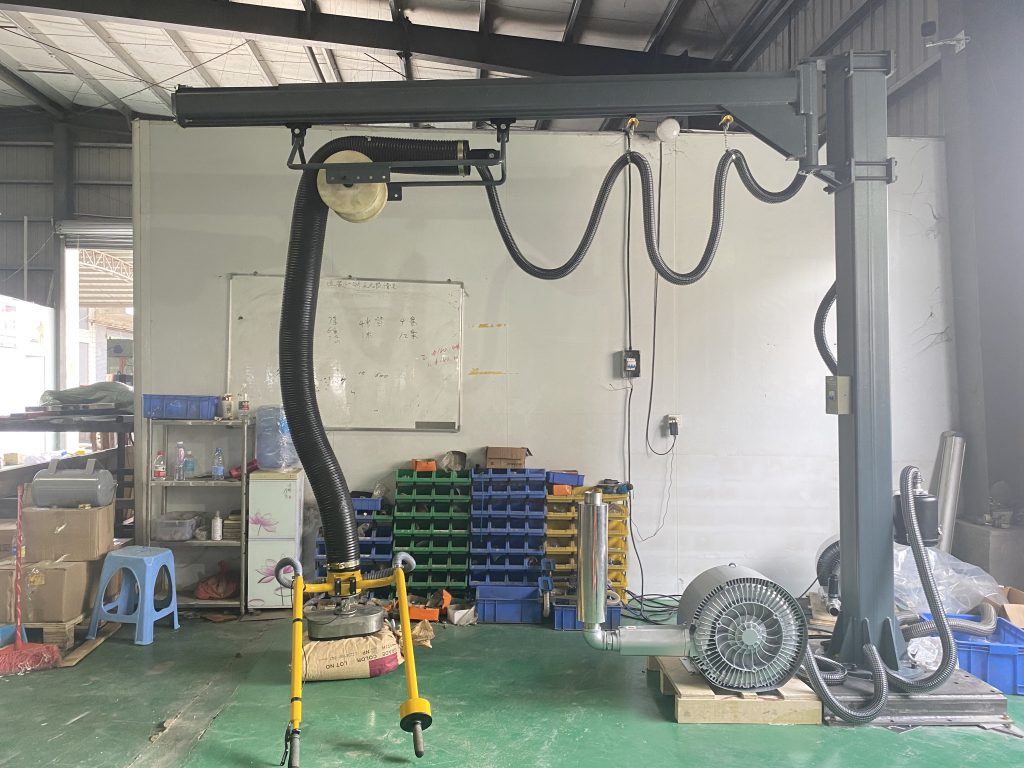

A vacuum suction lifter is a clever piece of equipment designed to make lifting and moving smooth, flat objects a breeze. It uses the power of suction to securely grip loads, offering a reliable and efficient way to handle materials without the need for manual heavy lifting.
Crafted for ease and safety, these lifters feature a suction pad or cup system, typically powered by pneumatic or electric vacuum pumps, that creates a strong seal on surfaces like glass, metal, or plastic. They’re perfect for tasks such as moving large panels, loading sheets onto machines, or positioning delicate items in industries like manufacturing, construction, or logistics. Valued for their gentle grip, speed, and ability to reduce strain, vacuum suction lifters are a go-to solution for boosting productivity while keeping workers safe.
Gantry-Style

Also known as linear manipulators or Cartesian cranes, gantry-style manipulators are robust machines designed to move heavy loads with remarkable precision, much like a coordinated grid in motion. They glide smoothly along straight paths, covering wide areas with ease, making them a top pick for industrial tasks that demand accuracy and strength.
These manipulators are built on a solid framework, often resembling an overhead bridge or track, with a movable arm or hoist that travels along three linear axes. Powered by electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems, they handle substantial loads like machinery components, pallets, or steel panels. Renowned for their swift movement, pinpoint precision, extensive reach, and adaptability to various workspace sizes, gantry-style manipulators excel in environments like manufacturing plants, warehouses, or shipyards, enhancing productivity while ensuring a safe and efficient workflow.
What industries are power manipulators used in?
Power-assisted robots are now widely used in the following industries:
Glass industry: glass, tempered glass, handling power-assisted robots, glass flipping power-assisted robots
Home panels: coffee table handling power-assisted robots, door and window handling robots, wooden board handling robots, tile handling robots
Electronic products industry: carton handling power-assisted robots, carton stacking power-assisted robots, pallet handling power-assisted robots, turnover boxes, circulation box power-assisted robots, server handling robots, LCD screen handling robots
Roller clamping: aluminum foil rolls, film rolls, handling power-assisted robots, internal expansion power-assisted robots, slitting machine unloading robots
Ceramic bathroom: toilets Handling assist robot, wash basin handling assist robot, bathtub handling assist robot
Sheet metal industry: plate, stainless steel, steel plate, fireproof board, stone slab, handling assist robot, laser feeding assist robot, electromagnetic suction assist robot, iron handling robot, metal liner handling robot
Chemical industry: iron barrel, plastic barrel, barrel handling assist robot, woven bag handling assist robot, barrel unloading assist arm, oil barrel, gas tank, handling assist robot
Automobile assembly: tire handling assist robot, battery handling assist robot, instrument panel assembly assist robot, welding tool loading and unloading assist robot, wheel hub Handling robot, seat handling assist robot, subframe handling robot, window and door assembly robot, engine housing handling robot, bumper handling robot, spring steel plate handling robot
New energy industry: transformer handling assist robot, battery pack handling assist robot, chassis handling assist robot, circuit breaker, radiator handling robot, gear handling robot
Food industry: stacking assist robot, carton stacking assist robot
Refractory brick production industry: refractory brick handling assist robot, press unloading assist robot, graphite crucible unloading assist robot
Machining industry: shaft handling assist robot, Machine tool loading and unloading assisting robot
Home appliance industry: refrigerator handling robot, water purifier handling robot, audio handling robot
Bagged products: bag handling robot, fertilizer handling robot, rice handling robot, sugar handling robot, cement handling robot
Steel pipe products: round pipe handling robot, column handling robot, silicon crystal rod handling robot, bar material handling robot
Wire and cable: cable handling robot, steel coil handling robot, I-wheel handling robot
Marble: marble handling robot, curbstone handling robot
Textile industry: cloth roll handling robot
Foundry industry: aluminum ingot, aluminum block, handling robot
Shopping for Robotic Arms?
Robotic arms are being produced today with a varied range of configurations to tailor to as many specific applications as possible. They are excelling in almost all industrial tasks, whether it’s swift movements for packaging, precise operations in manufacturing, or seamless collaboration with human workers.
RapidEfficient caters to this diverse range of robotic arm applications with its adaptable robotic arms and an extensive selection of accessories. creating an ecosystem that is both highly capable and user-friendly. Automation with RapidEfficient is cost-effective and easily accessible, and its robots not only meet specific requirements but also elevate overall productivity.
Industrial automation has surfaced as an innovative means for enterprises to maintain a competitive edge. Understanding their automation choices thoroughly empowers these businesses to seamlessly integrate them into their manufacturing processes and maximize efficiency.
Similar Blogs
Detailed classification of manipulators
Advantages of multi-joint manipulators The advantages of multi-joint manipulators are: flexible movements, small inertia, strong versatility, ability to grab workpieces close to the machine base,

How to improve the production accuracy of robotic hand?
Nowadays, many machinery manufacturers are choosing to use injection molding machine robots as their main production method. However, the use of automated robots in production
