In modern manufacturing, precision manufacturing machining centers are widely used for machining various parts due to their high precision, high efficiency, and high level of automation. Precision manufacturing machining centers can be categorized into three-axis, four-axis, and five-axis based on the number of motion axes. This article will detail the characteristics and application areas of three-axis, four-axis, and five-axis precision manufacturing machining centers to help readers better understand the differences between them.
Three-Axis Precision Manufacturing Machining Centers: Fundamentals and Efficiency
Three-axis precision manufacturing machining centers are the most traditional type of machining center, consisting of three linear motion axes: X, Y, and Z.
They are suitable for most routine grinding, drilling, and cutting operations. Three-axis machines excel at handling planar parts and simple three-dimensional parts, but may be limited when handling complex curved surfaces.
Four-Axis Precision Manufacturing Machining Centers: Increased Flexibility
Four-axis precision manufacturing machining centers add a rotary axis to the three axes, typically axis A or B.
This allows the machine to rotate the workpiece during machining, achieving more complex geometries.
Four-axis machines are suitable for machining parts with inclined planes or specific angle requirements.
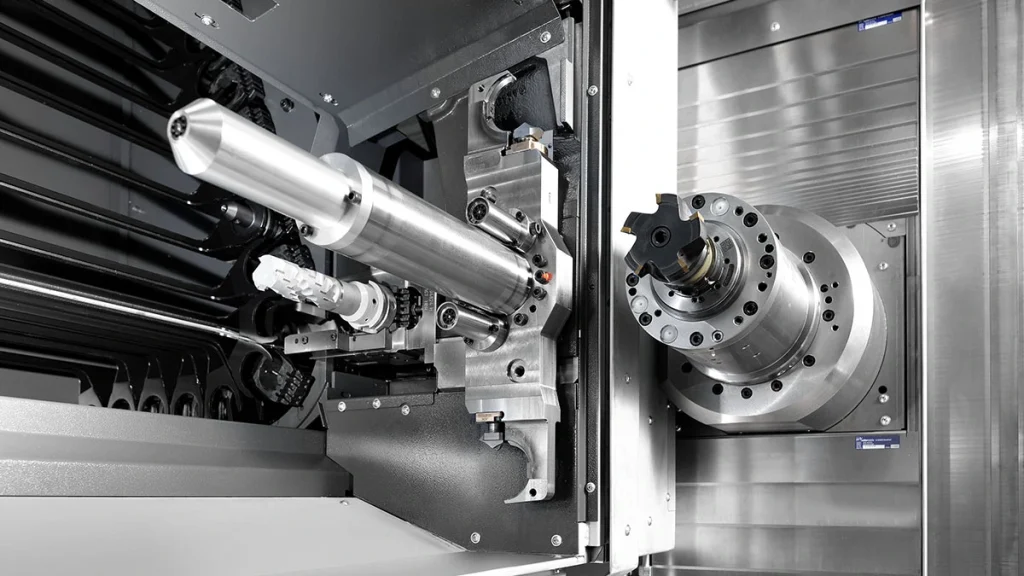
Five-Axis Precision Machining Centers: Solutions for Complex Machining
Five-axis precision machining centers consist of three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes (two of A, B, or C).
This configuration offers extremely high machining flexibility, allowing machining at virtually any angle within a single clamping position.
Five-axis machines are particularly well-suited for machining complex spatial surfaces, molds, and aerospace components.
Technical and Application Differences
- Machining Accuracy: As the number of axes increases, the machining accuracy and repeatability of the machine tool also improve.
- Machining Efficiency: Multi-axis machines can complete machining with fewer clamping operations, increasing productivity.
- Complexity: Three-axis machines are suitable for simple parts, while four-axis and five-axis machines are suitable for machining complex parts.
Cost: The more axes, the higher the purchase and maintenance costs of the machine.
Conclusion
Three-axis, four-axis, and five-axis precision machining centers each have their unique advantages and applicable areas. Three-axis precision machining centers are suitable for machining relatively simple parts, are low-cost, and easy to operate. Four-axis precision machining centers add a rotary axis to the three-axis configuration, enabling multi-axis machining and are suitable for machining complex parts. Five-axis precision machining centers have five-axis movement, enabling omnidirectional machining and are suitable for machining parts with high complexity and high precision requirements.
About RapidEfficient
RapidEfficient specializes in high-precision CNC machining with 18 years of experience.
Its products serve industries including medical, communications, optics, drones, intelligent robotics, automotive, and office automation parts.
The company’s CNC machining centers feature four-axis, five-axis, and multi-linkage machine tools, and are equipped with precision projectors, coordinate measuring machines (CMM), spectrometers, and other advanced inspection equipment.
Machining accuracy can reach 0.01 mm, and testing accuracy can reach 0.001 mm.






